构建一个即时消息应用(七):Access 页面

本文是该系列的第七篇。
现在我们已经完成了后端,让我们转到前端。 我将采用单页应用程序方案。
首先,我们创建一个 static/index.html 文件,内容如下。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Messenger</title>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="data:,">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles.css">
<script src="/main.js" type="module"></script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
这个 HTML 文件必须为每个 URL 提供服务,并且使用 JavaScript 负责呈现正确的页面。
因此,让我们将注意力转到 main.go 片刻,然后在 main() 函数中添加以下路由:
router.Handle("GET", "/...", http.FileServer(SPAFileSystem{http.Dir("static")}))
type SPAFileSystem struct {
fs http.FileSystem
}
func (spa SPAFileSystem) Open(name string) (http.File, error) {
f, err := spa.fs.Open(name)
if err != nil {
return spa.fs.Open("index.html")
}
return f, nil
}
我们使用一个自定义的文件系统,因此它不是为未知的 URL 返回 404 Not Found,而是转到 index.html。
路由器
在 index.html 中我们加载了两个文件:styles.css 和 main.js。我把样式留给你自由发挥。
让我们移动到 main.js。 创建一个包含以下内容的 static/main.js 文件:
import { guard } from './auth.js'
import Router from './router.js'
let currentPage
const disconnect = new CustomEvent('disconnect')
const router = new Router()
router.handle('/', guard(view('home'), view('access')))
router.handle('/callback', view('callback'))
router.handle(/^\/conversations\/([^\/]+)$/, guard(view('conversation'), view('access')))
router.handle(/^\//, view('not-found'))
router.install(async result => {
document.body.innerHTML = ''
if (currentPage instanceof Node) {
currentPage.dispatchEvent(disconnect)
}
currentPage = await result
if (currentPage instanceof Node) {
document.body.appendChild(currentPage)
}
})
function view(pageName) {
return (...args) => import(`/pages/${pageName}-page.js`)
.then(m => m.default(...args))
}
如果你是这个博客的关注者,你已经知道它是如何工作的了。 该路由器就是在 这里 显示的那个。 只需从 @nicolasparada/router 下载并保存到 static/router.js 即可。
我们注册了四条路由。 在根路由 / 处,我们展示 home 或 access 页面,无论用户是否通过身份验证。 在 /callback 中,我们展示 callback 页面。 在 /conversations/{conversationID} 上,我们展示对话或 access 页面,无论用户是否通过验证,对于其他 URL,我们展示一个 not-found 页面。
我们告诉路由器将结果渲染为文档主体,并在离开之前向每个页面调度一个 disconnect 事件。
我们将每个页面放在不同的文件中,并使用新的动态 import() 函数导入它们。
身份验证
guard() 是一个函数,给它两个函数作为参数,如果用户通过了身份验证,则执行第一个函数,否则执行第二个。它来自 auth.js,所以我们创建一个包含以下内容的 static/auth.js 文件:
export function isAuthenticated() {
const token = localStorage.getItem('token')
const expiresAtItem = localStorage.getItem('expires\_at')
if (token === null || expiresAtItem === null) {
return false
}
const expiresAt = new Date(expiresAtItem)
if (isNaN(expiresAt.valueOf()) || expiresAt <= new Date()) {
return false
}
return true
}
export function guard(fn1, fn2) {
return (...args) => isAuthenticated()
? fn1(...args)
: fn2(...args)
}
export function getAuthUser() {
if (!isAuthenticated()) {
return null
}
const authUser = localStorage.getItem('auth\_user')
if (authUser === null) {
return null
}
try {
return JSON.parse(authUser)
} catch (_) {
return null
}
}
isAuthenticated() 检查 localStorage 中的 token 和 expires_at,以判断用户是否已通过身份验证。getAuthUser() 从 localStorage 中获取经过身份验证的用户。
当我们登录时,我们会将所有的数据保存到 localStorage,这样才有意义。
Access 页面

让我们从 access 页面开始。 创建一个包含以下内容的文件 static/pages/access-page.js:
const template = document.createElement('template')
template.innerHTML = `
<h1>Messenger</h1>
<a href="/api/oauth/github" onclick="event.stopPropagation()">Access with GitHub</a>
`
export default function accessPage() {
return template.content
}
因为路由器会拦截所有链接点击来进行导航,所以我们必须特别阻止此链接的事件传播。
单击该链接会将我们重定向到后端,然后重定向到 GitHub,再重定向到后端,然后再次重定向到前端; 到 callback 页面。
Callback 页面
创建包括以下内容的 static/pages/callback-page.js 文件:
import http from '../http.js'
import { navigate } from '../router.js'
export default async function callbackPage() {
const url = new URL(location.toString())
const token = url.searchParams.get('token')
const expiresAt = url.searchParams.get('expires\_at')
try {
if (token === null || expiresAt === null) {
throw new Error('Invalid URL')
}
const authUser = await getAuthUser(token)
localStorage.setItem('auth\_user', JSON.stringify(authUser))
localStorage.setItem('token', token)
localStorage.setItem('expires\_at', expiresAt)
} catch (err) {
alert(err.message)
} finally {
navigate('/', true)
}
}
function getAuthUser(token) {
return http.get('/api/auth\_user', { authorization: `Bearer ${token}` })
}
callback 页面不呈现任何内容。这是一个异步函数,它使用 URL 查询字符串中的 token 向 /api/auth_user 发出 GET 请求,并将所有数据保存到 localStorage。 然后重定向到 /。
HTTP
这里是一个 HTTP 模块。 创建一个包含以下内容的 static/http.js 文件:
import { isAuthenticated } from './auth.js'
async function handleResponse(res) {
const body = await res.clone().json().catch(() => res.text())
if (res.status === 401) {
localStorage.removeItem('auth\_user')
localStorage.removeItem('token')
localStorage.removeItem('expires\_at')
}
if (!res.ok) {
const message = typeof body === 'object' && body !== null && 'message' in body
? body.message
: typeof body === 'string' && body !== ''
? body
: res.statusText
throw Object.assign(new Error(message), {
url: res.url,
statusCode: res.status,
statusText: res.statusText,
headers: res.headers,
body,
})
}
return body
}
function getAuthHeader() {
return isAuthenticated()
? { authorization: `Bearer ${localStorage.getItem('token')}` }
: {}
}
export default {
get(url, headers) {
return fetch(url, {
headers: Object.assign(getAuthHeader(), headers),
}).then(handleResponse)
},
post(url, body, headers) {
const init = {
method: 'POST',
headers: getAuthHeader(),
}
if (typeof body === 'object' && body !== null) {
init.body = JSON.stringify(body)
init.headers['content-type'] = 'application/json; charset=utf-8'
}
Object.assign(init.headers, headers)
return fetch(url, init).then(handleResponse)
},
subscribe(url, callback) {
const urlWithToken = new URL(url, location.origin)
if (isAuthenticated()) {
urlWithToken.searchParams.set('token', localStorage.getItem('token'))
}
const eventSource = new EventSource(urlWithToken.toString())
eventSource.onmessage = ev => {
let data
try {
data = JSON.parse(ev.data)
} catch (err) {
console.error('could not parse message data as JSON:', err)
return
}
callback(data)
}
const unsubscribe = () => {
eventSource.close()
}
return unsubscribe
},
}
这个模块是 fetch 和 EventSource API 的包装器。最重要的部分是它将 JSON web 令牌添加到请求中。
Home 页面

因此,当用户登录时,将显示 home 页。 创建一个具有以下内容的 static/pages/home-page.js 文件:
import { getAuthUser } from '../auth.js'
import { avatar } from '../shared.js'
export default function homePage() {
const authUser = getAuthUser()
const template = document.createElement('template')
template.innerHTML = `
<div>
<div>
${avatar(authUser)}
<span>${authUser.username}</span>
</div>
<button id="logout-button">Logout</button>
</div>
<!-- conversation form here -->
<!-- conversation list here -->
`
const page = template.content
page.getElementById('logout-button').onclick = onLogoutClick
return page
}
function onLogoutClick() {
localStorage.clear()
location.reload()
}
对于这篇文章,这是我们在 home 页上呈现的唯一内容。我们显示当前经过身份验证的用户和注销按钮。
当用户单击注销时,我们清除 localStorage 中的所有内容并重新加载页面。
Avatar
那个 avatar() 函数用于显示用户的头像。 由于已在多个地方使用,因此我将它移到 shared.js 文件中。 创建具有以下内容的文件 static/shared.js:
export function avatar(user) {
return user.avatarUrl === null
? `<figure class="avatar" data-initial="${user.username[0]}"></figure>`
: `<img class="avatar" src="${user.avatarUrl}" alt="${user.username}'s avatar">`
}
如果头像网址为 null,我们将使用用户的姓名首字母作为初始头像。
你可以使用 attr() 函数显示带有少量 CSS 样式的首字母。
.avatar[data-initial]::after {
content: attr(data-initial);
}
仅开发使用的登录
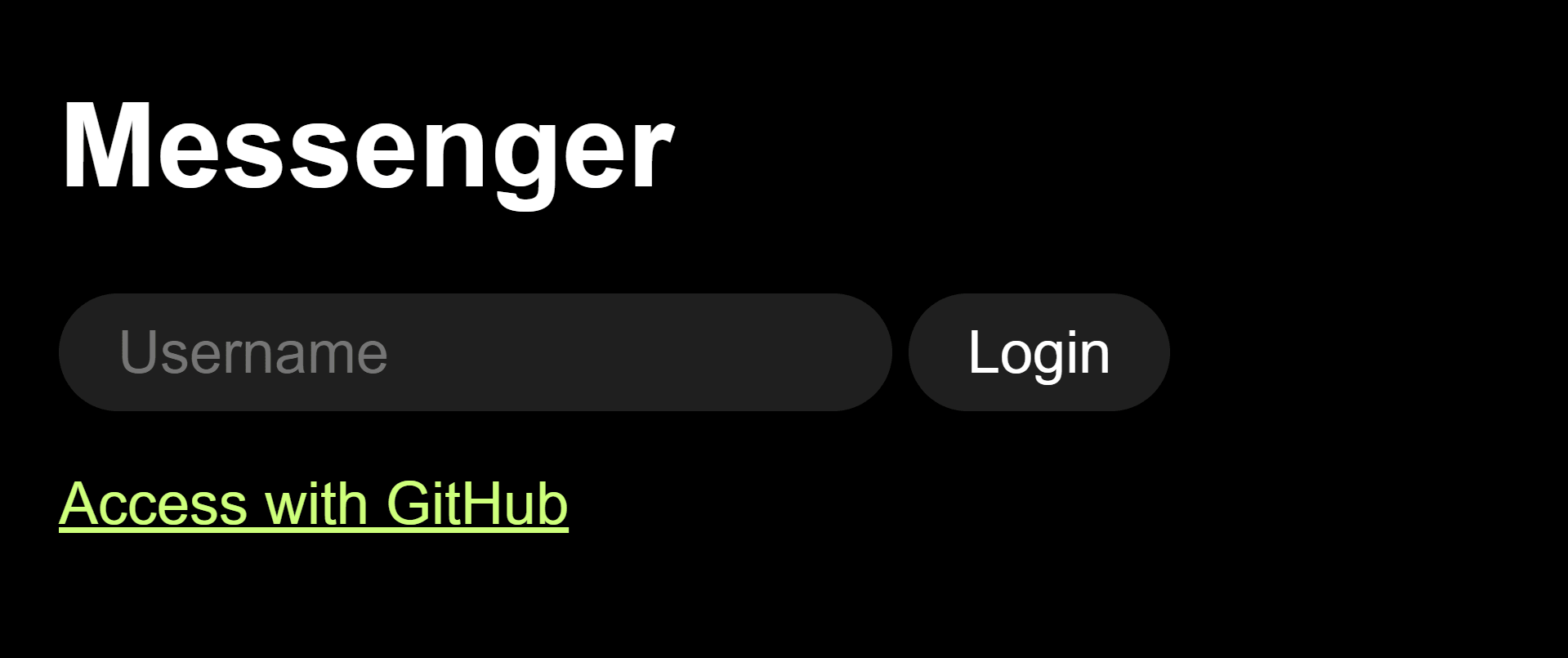
在上一篇文章中,我们为编写了一个登录代码。让我们在 access 页面中为此添加一个表单。 进入 static/ages/access-page.js,稍微修改一下。
import http from '../http.js'
const template = document.createElement('template')
template.innerHTML = `
<h1>Messenger</h1>
<form id="login-form">
<input type="text" placeholder="Username" required>
<button>Login</button>
</form>
<a href="/api/oauth/github" onclick="event.stopPropagation()">Access with GitHub</a>
`
export default function accessPage() {
const page = template.content.cloneNode(true)
page.getElementById('login-form').onsubmit = onLoginSubmit
return page
}
async function onLoginSubmit(ev) {
ev.preventDefault()
const form = ev.currentTarget
const input = form.querySelector('input')
const submitButton = form.querySelector('button')
input.disabled = true
submitButton.disabled = true
try {
const payload = await login(input.value)
input.value = ''
localStorage.setItem('auth\_user', JSON.stringify(payload.authUser))
localStorage.setItem('token', payload.token)
localStorage.setItem('expires\_at', payload.expiresAt)
location.reload()
} catch (err) {
alert(err.message)
setTimeout(() => {
input.focus()
}, 0)
} finally {
input.disabled = false
submitButton.disabled = false
}
}
function login(username) {
return http.post('/api/login', { username })
}
我添加了一个登录表单。当用户提交表单时。它使用用户名对 /api/login 进行 POST 请求。将所有数据保存到 localStorage 并重新加载页面。
记住在前端完成后删除此表单。
这就是这篇文章的全部内容。在下一篇文章中,我们将继续使用主页添加一个表单来开始对话,并显示包含最新对话的列表。
via: https://nicolasparada.netlify.com/posts/go-messenger-access-page/
作者:Nicolás Parada 选题:lujun9972 译者:gxlct008 校对:wxy