如何在 Linux 中重置 MySQL 或者 MariaDB 的 root 密码
如果你是第一次设置 MySQL 或 MariaDB 数据库,你可以直接运行 mysql_secure_installation 来实现基本的安全设置。

其中一项是设置数据库 root 帐户的密码 - 你必须保持私密,并仅在绝对需要时使用。如果你忘记了密码或需要重置密码(例如,当数据库管理员换人或被裁员!),这篇文章会派上用场。我们将解释如何在 Linux 中重置或恢复 MySQL 或 MariaDB 的 root 密码。
建议阅读: 更改 MySQL 或 MariaDB 的 root 密码。
虽然我们将在本文中使用 MariaDB,但这些说明同样也适用于 MySQL。
恢复 MySQL 或者 MariaDB 的 root 密码
开始之前,先停止数据库服务并检查服务状态,我们应该可以看到先前设置的环境变量:
------------- SystemD -------------
# systemctl stop mariadb
------------- SysVinit -------------
# /etc/init.d/mysqld stop
接下来,用 --skip-grant-tables 选项启动服务:
------------- SystemD -------------
# systemctl set-environment MYSQLD_OPTS="--skip-grant-tables"
# systemctl start mariadb
# systemctl status mariadb
------------- SysVinit -------------
# mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
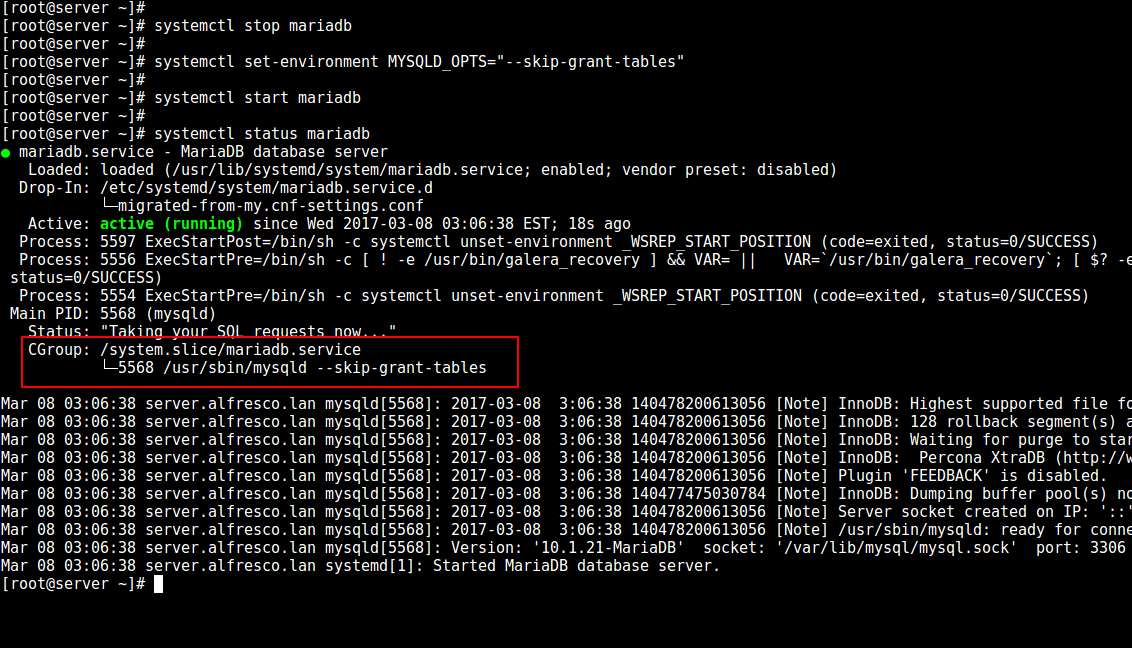
使用 skip tables 启动 MySQL/MariaDB
这可以让你不用 root 密码就能连接到数据库(你也许需要切换到另外一个终端上):
# mysql -u root
接下来,按照下面列出的步骤来。
MariaDB [(none)]> USE mysql;
MariaDB [(none)]> UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD('YourNewPasswordHere') WHERE User='root' AND Host = 'localhost';
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
最后,停止服务,取消环境变量设置并再次启动服务:
------------- SystemD -------------
# systemctl stop mariadb
# systemctl unset-environment MYSQLD_OPTS
# systemctl start mariadb
------------- SysVinit -------------
# /etc/init.d/mysql stop
# /etc/init.d/mysql start
这可以让先前的改变生效,允许你使用新的密码连接到数据库。
总结
本文我们讨论了如何重置 MariaDB/MySQL 的 root 密码。一如往常,如果你有任何问题或反馈请在评论栏中给我们留言。我们期待听到你的声音。
作者简介:
Gabriel Cánepa - 一位来自阿根廷圣路易斯梅塞德斯镇 (Villa Mercedes, San Luis, Argentina) 的 GNU/Linux 系统管理员,Web 开发者。就职于一家世界领先级的消费品公司,乐于在每天的工作中能使用 FOSS 工具来提高生产力。
via: http://www.tecmint.com/reset-mysql-or-mariadb-root-password/
作者:Gabriel Cánepa 译者:geekpi 校对:jasminepeng