如何在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS安装网络爬虫工具:Scrapy
这是一款提取网站数据的开源工具。Scrapy框架用Python开发而成,它使抓取工作又快又简单,且可扩展。我们已经在virtual box中创建一台虚拟机(VM)并且在上面安装了Ubuntu 14.04 LTS。
安装 Scrapy

Scrapy依赖于Python、开发库和pip。Python最新的版本已经在Ubuntu上预装了。因此我们在安装Scrapy之前只需安装pip和python开发库就可以了。
pip是作为python包索引器easy_install的替代品,用于安装和管理Python包。pip包的安装可见图 1。
sudo apt-get install python-pip
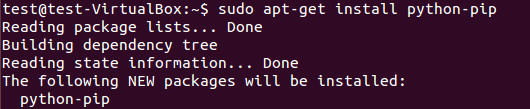
图:1 pip安装
我们必须要用下面的命令安装python开发库。如果包没有安装那么就会在安装scrapy框架的时候报关于python.h头文件的错误。
sudo apt-get install python-dev
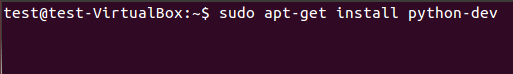
图:2 Python 开发库
scrapy框架既可从deb包安装也可以从源码安装。在图3中我们用pip(Python 包管理器)安装了deb包了。
sudo pip install scrapy
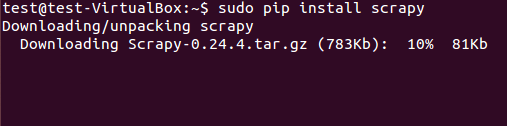
图:3 Scrapy 安装
图4中scrapy的成功安装需要一些时间。
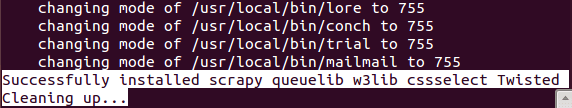
图:4 成功安装Scrapy框架
使用scrapy框架提取数据
基础教程
我们将用scrapy从fatwallet.com上提取商店名称(卖卡的店)。首先,我们使用下面的命令新建一个scrapy项目“store name”, 见图5。
$sudo scrapy startproject store_name
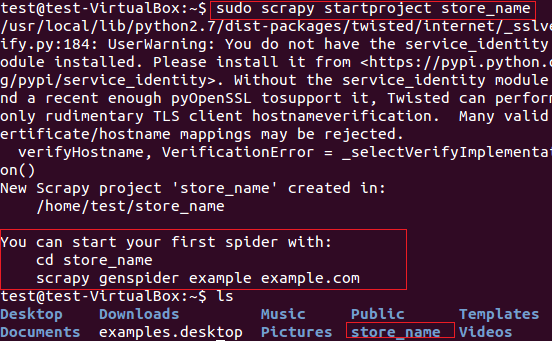
图:5 Scrapy框架新建项目
上面的命令在当前路径创建了一个“store_name”的目录。项目主目录下包含的文件/文件夹见图6。
$sudo ls –lR store_name
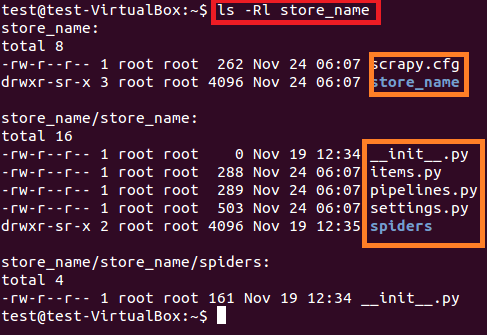
图:6 store_name项目的内容
每个文件/文件夹的概要如下:
- scrapy.cfg 是项目配置文件
- store_name/ 主目录下的另一个文件夹。 这个目录包含了项目的python代码
- store_name/items.py 包含了将由蜘蛛爬取的项目
- store_name/pipelines.py 是管道文件
- store_name/settings.py 是项目的配置文件
- store_name/spiders/, 包含了用于爬取的蜘蛛
由于我们要从fatwallet.com上如提取店名,因此我们如下修改文件(LCTT 译注:这里没说明是哪个文件,译者认为应该是 items.py)。
import scrapy
class StoreNameItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field() # 取出卡片商店的名称
之后我们要在项目的store_name/spiders/文件夹下写一个新的蜘蛛。蜘蛛是一个python类,它包含了下面几个必须的属性:
- 蜘蛛名 (name )
- 爬取起点url (start_urls)
- 包含了从响应中提取需要内容相应的正则表达式的解析方法。解析方法对爬虫而言很重要。
我们在storename/spiders/目录下创建了“storename.py”爬虫,并添加如下的代码来从fatwallet.com上提取店名。爬虫的输出写到文件(StoreName.txt)中,见图7。
from scrapy.selector import Selector
from scrapy.spider import BaseSpider
from scrapy.http import Request
from scrapy.http import FormRequest
import re
class StoreNameItem(BaseSpider):
name = "storename"
allowed_domains = ["fatwallet.com"]
start_urls = ["http://fatwallet.com/cash-back-shopping/"]
def parse(self,response):
output = open('StoreName.txt','w')
resp = Selector(response)
tags = resp.xpath('//tr[@class="storeListRow"]|\
//tr[@class="storeListRow even"]|\
//tr[@class="storeListRow even last"]|\
//tr[@class="storeListRow last"]').extract()
for i in tags:
i = i.encode('utf-8', 'ignore').strip()
store_name = ''
if re.search(r"class=\"storeListStoreName\">.*?<",i,re.I|re.S):
store_name = re.search(r"class=\"storeListStoreName\">.*?<",i,re.I|re.S).group()
store_name = re.search(r">.*?<",store_name,re.I|re.S).group()
store_name = re.sub(r'>',"",re.sub(r'<',"",store_name,re.I))
store_name = re.sub(r'&',"&",re.sub(r'&',"&",store_name,re.I))
#print store_name
output.write(store_name+""+"\n")
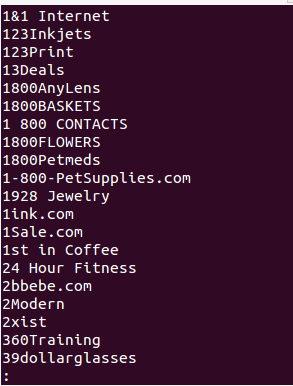
图:7 爬虫的输出
注意: 本教程的目的仅用于理解scrapy框架
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/scrapy-install-ubuntu/